Installer Raspberry Pi OS
Créer la carte SD (Windows)
Télécharger l'archive
- Téléchargez l'archive
Raspberry Pi OS ... Lite - Décompressez l'archive pour obtenir un fichier
.img - Insérez la carte
SD
Créer la carte SD avec Rufus
- Téléchargez
Rufus X.XX Portable - Exécuter
Rufusen tant qu'administrateur - Sélectionnez le lecteur de la carte
SD, le fichier image, puis cliquez surDémarrer
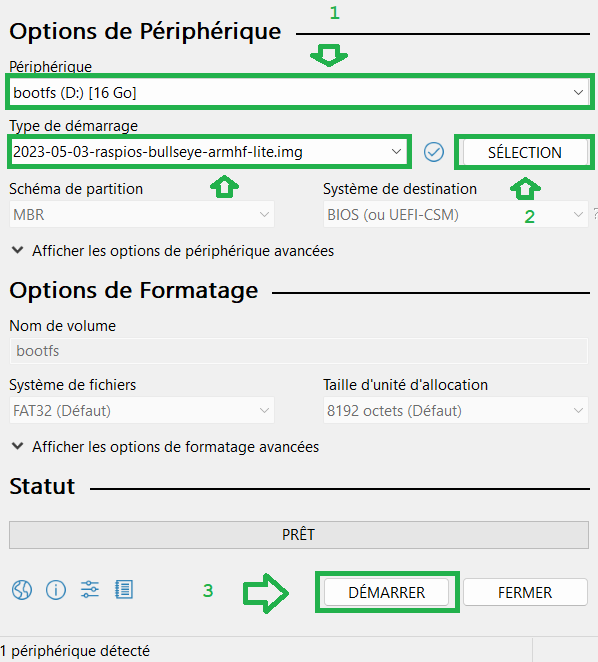
- Une fois que le
Statutpasse à l'étatPRÊT, cliquez surFermer
Effectuer la post installation (avec un clavier et une souris)
- Insérez la carte SD dans le Raspberry PI.
- Reliez le Raspberry PI à un clavier. (Pour accéder au
RPisans clavier, consultez : Installer Raspbian sans écran ni clavier.) - Reliez le Raspberry PI à un écran en fonction du câble vidéo fourni.
- Allumez l'écran
- Connectez l'alimentation du Raspberry PI (prise micro-usb)
- Le Raspberry PI démarre.
Configuring Keyboard configurationOtherFrenchFrenchPlease enter new user name- Créez un utilisateur (dans l'exemple ci-dessous l'utilisateur s'appelle x)
Please set a password for XPlease confirm the password- Connectez-vous :
rapberrypi login : Xpassword :(le mot de passe n'est pas affiché)
Activer le serveur ssh
Il faut utiliser la commnde systemctl
- enable : active le serveur ssh au démarrage
- start : active le serveur ssh immédiatement
x@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo systemctl enable ssh x@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo systemctl start ssh
Renommer le RPi
Dans l'exemple ci-dessous le nouveau nom du Raspberry Pi est : rpiX
- Modifier le nom du Raspberry Pi
x@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname rpiX
- Modifier la correspondance adresse IP <-> nom dans le fichier /etc/hosts pour
l'adresse IP
127.0.1.1en indiquent le nom de votre Raspberry Pi. Ne modifiez surtour pas les autres lignes.
- (Remarque, il faut taper
ESCpuisCtrl+XpuisY(Yes) pour sauvegarder dans nano)
x@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 127.0.1.1 rpiX
- Redémarrez le serveur
x@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo shutdown -r now
- Après redémarrage
x@rpiX:~$

